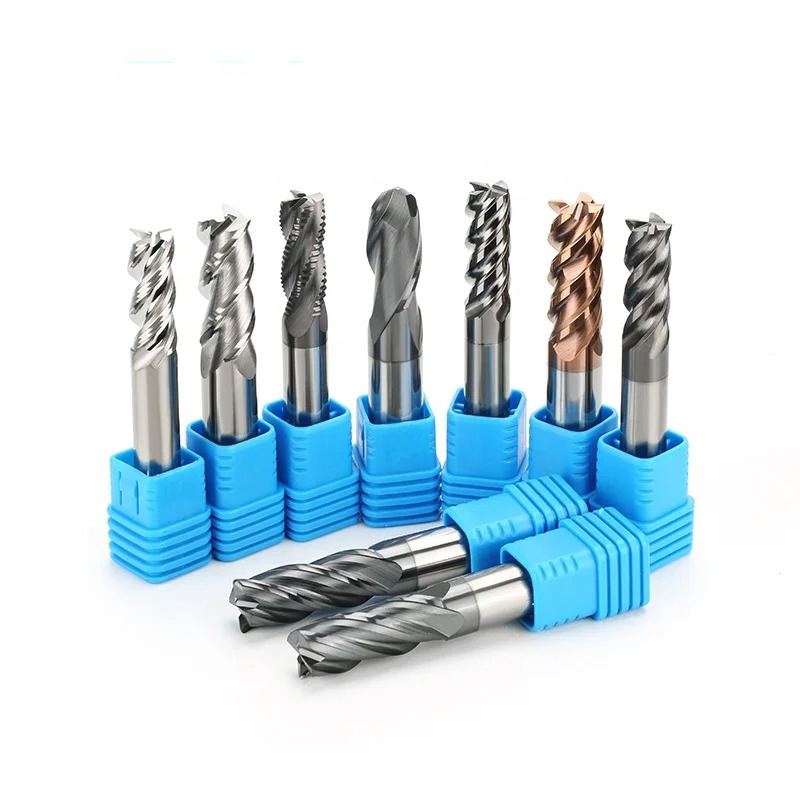
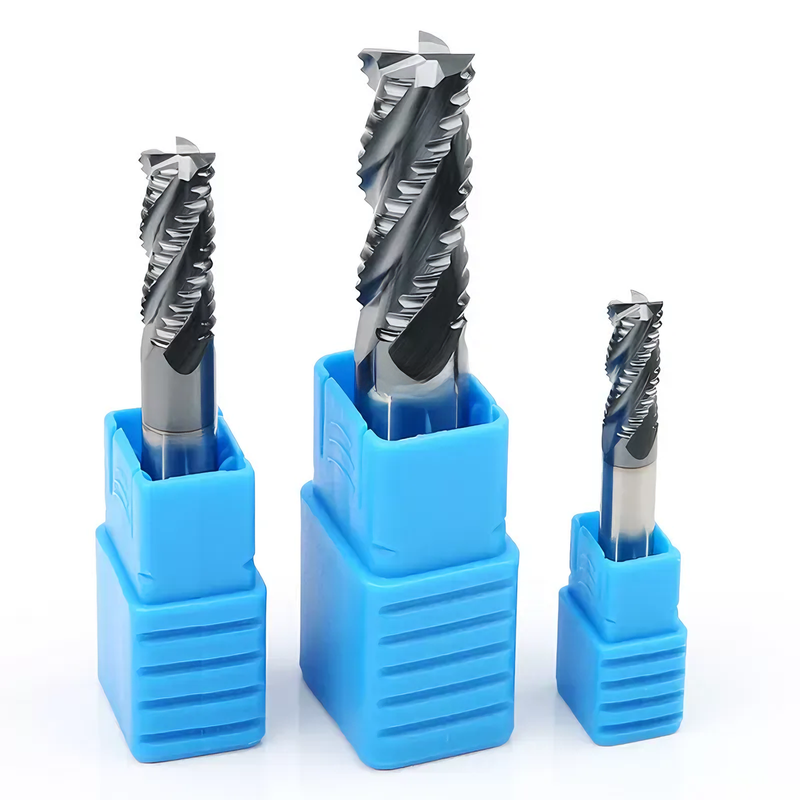
End mills are among the most important cutting tools in CNC machining. They are used every day in industries such as automotive, aerospace, mold and die, medical manufacturing, and general machining. However, for many beginners and even experienced buyers, understanding the differences between end mill types, coatings, and applications can be confusing.

This guide is designed to help you clearly understand end mill types, explain why coatings matter, and share practical tips to maximize performance, especially when using carbide square end mills, one of the most widely used end mill designs.
After reading this article, you will be able to:
- Identify common end mill types and their applications
- Understand different coatings and when to use them
- Learn why carbide square end mills are so popular
- Apply practical tips to improve tool life and machining results
1. What Is an End Mill?
An end mill is a rotating cutting tool used in milling machines and CNC machining centers to remove material from a workpiece. Unlike drill bits, which cut only in the downward direction, end mills can cut:
- From the side
- From the bottom
- Along curved or complex paths
This makes end mills highly versatile for shaping parts, creating slots, pockets, profiles, and 3D surfaces.
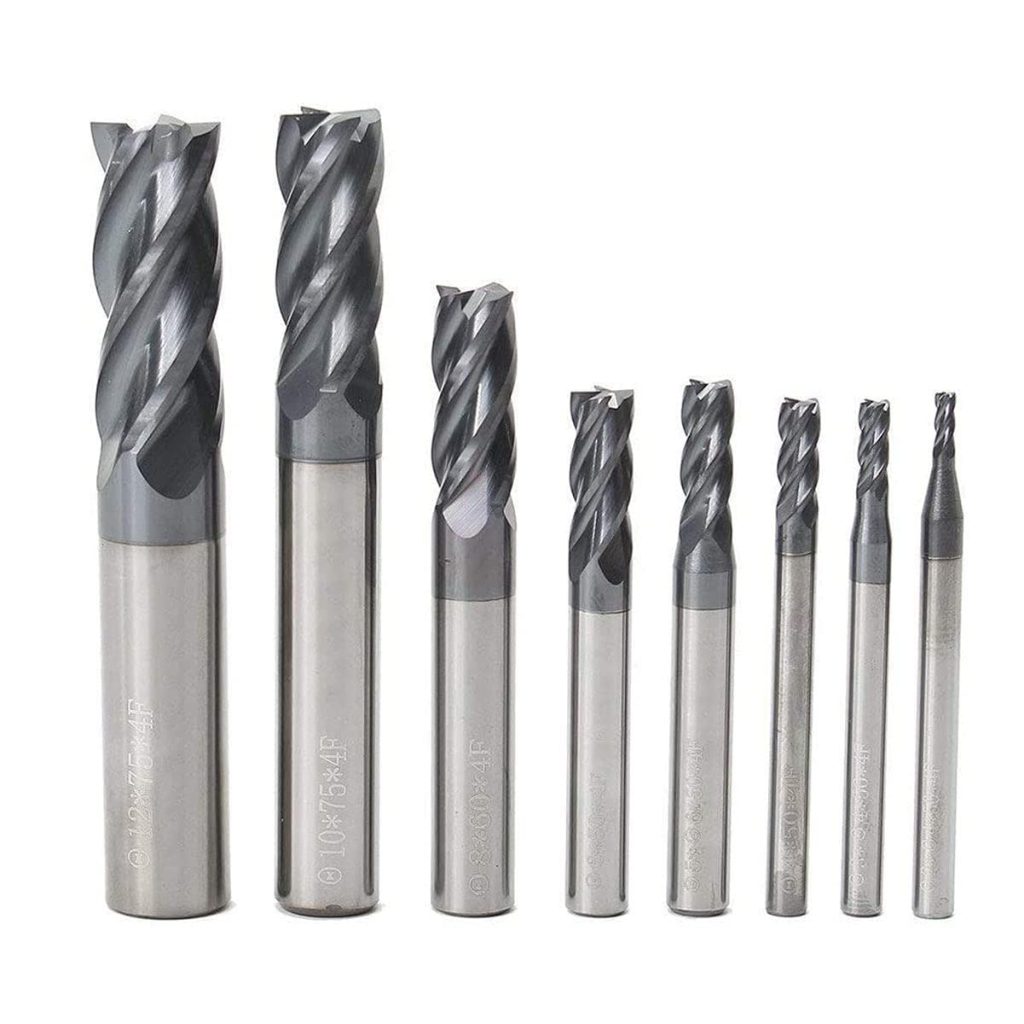

2. Common Types of End Mills
Understanding end mill types is the first step to choosing the right tool.
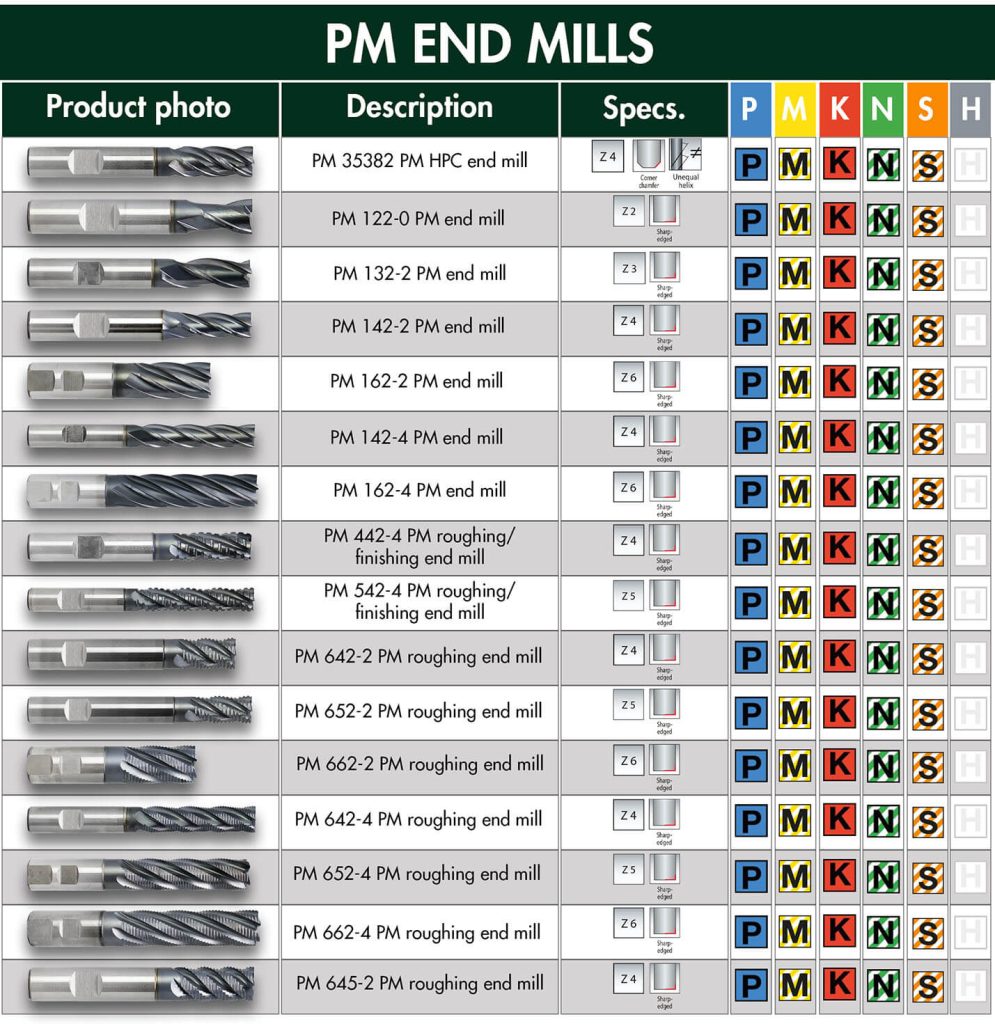
2.1 Square End Mills
Square end mills have a flat bottom and sharp 90-degree corners. They are the most commonly used end mills in CNC machining.
Typical uses:
- Slotting
- Pocket milling
- Side milling
- General-purpose machining
Because of their versatility, square end mills are often the first choice for beginners and production environments alike.
2.2 Ball Nose End Mills
Ball nose end mills feature a rounded cutting tip.
Typical uses:
- 3D contouring
- Mold and die machining
- Curved surfaces
They are not ideal for heavy material removal but are excellent for finishing and complex shapes.
2.3 Corner Radius End Mills
Corner radius end mills look similar to square end mills but have a small radius at the corners.
Advantages:
- Stronger cutting edges
- Reduced chipping
- Longer tool life
They are commonly used for semi-finishing and finishing operations.
2.4 Roughing End Mills
Roughing end mills have serrated or wavy cutting edges.
Purpose:
- Fast material removal
- Reduced cutting forces
- Shorter cycle times
They are typically followed by finishing tools to achieve final dimensions.
2.5 Chamfer and Specialty End Mills
These include chamfer end mills, thread mills, and form cutters, each designed for specific tasks such as edge breaking, threading, or profiling.
3. Why Carbide Is the Preferred Tool Material
End mills can be made from different materials, but solid carbide is the most widely used in modern CNC machining.
Benefits of Carbide End Mills
- High hardness and wear resistance
- Excellent heat resistance
- Suitable for high-speed machining
- Better dimensional stability
Compared to high-speed steel (HSS), carbide end mills provide longer tool life and more consistent performance, especially in CNC environments.
4. Understanding Carbide Square End Mills
Carbide square end mills combine the strength of solid carbide with the versatility of a flat cutting bottom and sharp corners.
Why They Are So Popular
- Suitable for a wide range of materials
- Easy to program
- Available in many sizes and configurations
- Reliable for both roughing and finishing
For many CNC shops and distributors, carbide square end mills form the core of their tooling inventory.
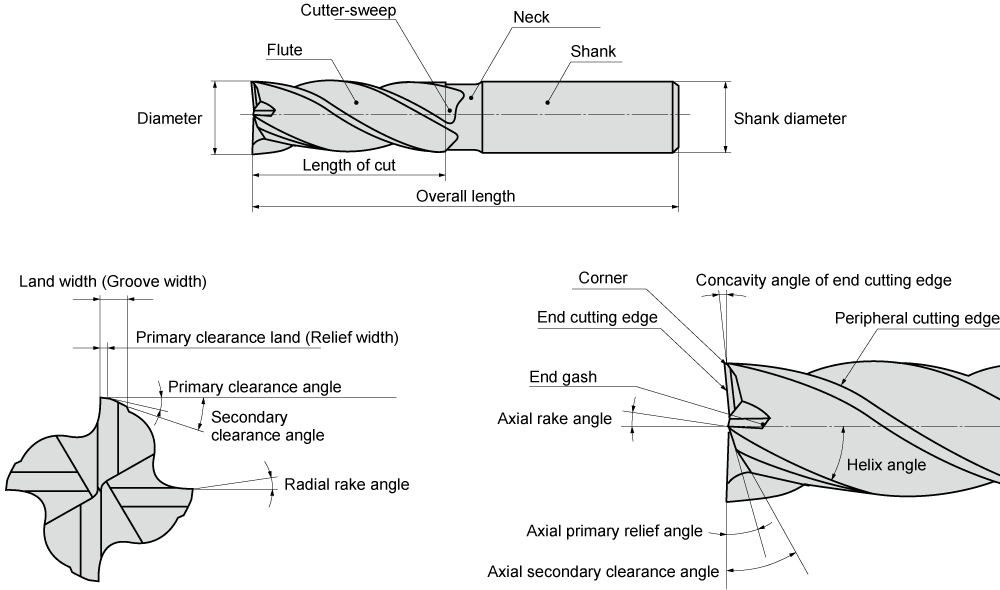
5. Key Design Elements of Carbide Square End Mills
Understanding the structure helps you select the right tool.
5.1 Flute Count
- 2 flutes: Better chip evacuation, ideal for aluminum
- 3 flutes: Balanced strength and chip space
- 4 flutes: Stronger edges, suitable for steel
5.2 Helix Angle
A higher helix angle provides smoother cutting and better surface finish, while a lower helix angle offers stronger cutting edges.
5.3 Cutting Length and Overall Length
Shorter tools provide better rigidity. Longer tools are used only when necessary for deep pockets or reach.
6. Common Coatings for End Mills
Coatings play a major role in tool performance by reducing friction, heat, and wear.
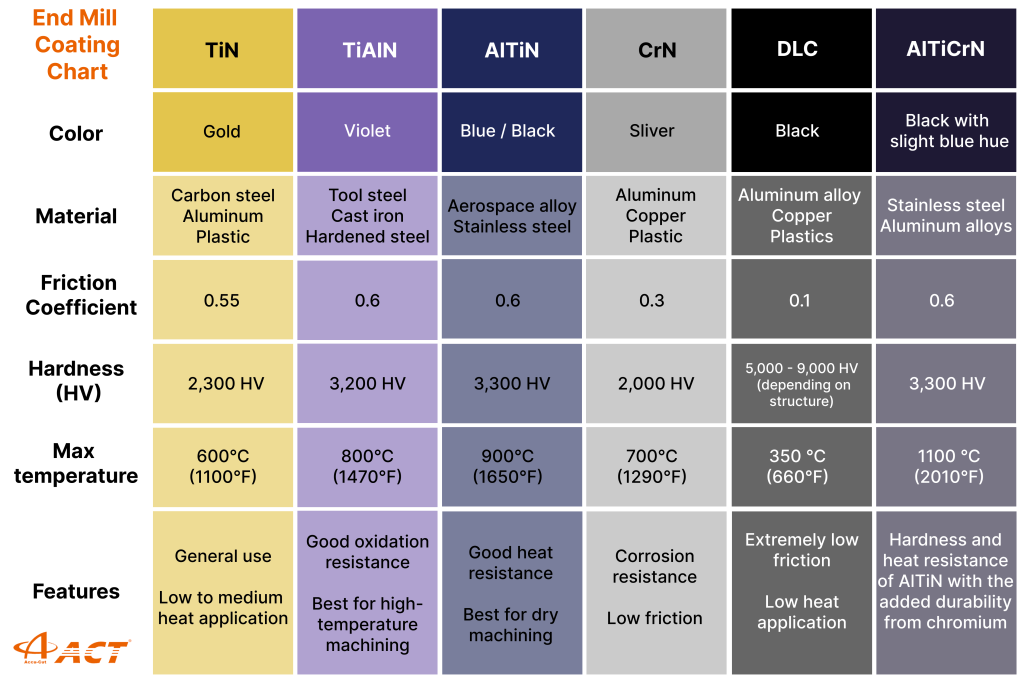
6.1 Uncoated
- Best for aluminum and plastics
- Sharp cutting edges
- Lower cost
6.2 TiN (Titanium Nitride)
- General-purpose coating
- Improves wear resistance
- Gold-colored appearance
6.3 TiAlN / AlTiN
- High-temperature resistance
- Ideal for steel and stainless steel
- Suitable for dry or high-speed machining
6.4 AlCrN
- Excellent heat and oxidation resistance
- Used for heavy-duty machining and hard materials
6.5 DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)
- Very low friction
- Excellent for aluminum and non-ferrous materials
7. How to Choose the Right Coating
Selecting the right coating depends on:
- Workpiece material
- Cutting speed
- Cooling method
General guidance:
- Aluminum → uncoated or DLC
- Steel → TiAlN or AlCrN
- Stainless steel → TiAlN with stable cutting parameters
Using the wrong coating can lead to chip buildup, excessive heat, or premature wear.
8. Tips to Get the Most from Carbide Square End Mills
Tip 1: Choose the Largest Possible Diameter
Larger diameters reduce deflection and vibration, improving surface finish and tool life.
Tip 2: Use the Shortest Tool Length
Shorter tools are more rigid and allow higher cutting parameters.
Tip 3: Match Flute Count to Material
Too many flutes in soft materials cause chip packing. Too few flutes in hard materials reduce strength.
Tip 4: Optimize Cutting Parameters
Follow supplier recommendations for speeds and feeds, then fine-tune based on machine rigidity and results.
Tip 5: Use Proper Tool Holders
High-quality tool holders reduce runout, which directly affects tool life and surface finish.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using aluminum tools on steel
- Selecting long tools unnecessarily
- Ignoring coating recommendations
- Running too slow or too fast
- Focusing only on tool price
Avoiding these mistakes often leads to immediate performance improvement.
10. Applications of Carbide Square End Mills
Carbide square end mills are widely used in:
- Automotive components
- Aerospace structures
- Mold bases
- Fixtures and jigs
- General CNC machining
Their flexibility makes them suitable for both small job shops and large-scale production.
11. How This Knowledge Helps You Choose from Our Product List
By understanding:
- End mill types
- Coatings
- Geometry
- Application needs
you can quickly identify the right carbide square end mill from our product listings. Each product page provides information on:
- Recommended materials
- Flute count
- Coating options
- Dimensions
This allows confident and efficient tool selection.
12. Final Thoughts
Understanding end mill types and coatings is not just technical knowledge — it directly impacts machining quality, productivity, and cost.
Carbide square end mills remain one of the most reliable and versatile cutting tools in CNC machining. When selected correctly and used properly, they deliver excellent performance across a wide range of applications.
For best results, always match the tool to the material, operation, and machine capability, and work with a supplier who provides consistent quality and technical support.



